Configuring Channel Settings
You need rights to modify the channel you configure (voice, e-mail, or chat).
The defined settings are inherited from the channel level to the queue level. You can also define some of the channel settings at the queue level. These settings are marked with an asterisk (*) in the queue settings. An empty field or the option Not Defined in the queue settings means that the setting follows the channel setting. If you define the value at the queue level, it overrides the channel setting for this queue.
When defining Extra Data Settings, notice that call attached data (CAD) used for customer indentification is subject for manipulation. We recommend using two-factor authentication.
- On the System Configurator main screen, choose .
- Choose the channel.
- Configure the settings according to the following tables. The tables below
refer to parameter groups that may appear in different order on the user
interface for different channels (voice, e-mail and chat).
Table 1. Contact Management Settings Channel Type
Field
Function
Voice
Use Early Queuing
To activate early queuing in the voice channel, select this option. The function must be enabled in Advanced Settings in .
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Timeout for Contacts to be Picked or Rejected
Enter a time to define how long a conversation is being offered in Communication Panel or Communication Desktop (CDT). The default value is 120000 (2 minutes).
The queue-level value must be less than the one defined for the channel.
Automatic Not Ready Status in Communication Panel
To change the agent status to not ready when the defined time has elapsed if the agent hasn't responded to the offering with the Accept or Reject buttons, define the following settings:- Timeout for Contacts to be Picked or Rejected in
- Activate Not Ready After No Response in
- Number of Offerings Before Activing Not Ready in
Timeout in Communication Desktop (CDT)
If you define timeout for contacts also in , CDT follows the user setting. For example, if Timeout for Contacts to be Picked or Rejected is 2 minutes and Answer Timeout for Queue Contacts 30 seconds, CDT rejects a queue contact after 30 seconds. CEM stops allocating it after 2 minutes.
Voice
Non-Autom. Connection
Optional for advanced use: enter a comma-separated list of commands which do not cause the call to be connected when Early Queuing is in use. Possible commands are CALL_TRANSFER, CALL_JOIN, and GENERATE_DTMF.
Voice
DTMF Character for Forwarding
Enter the DTMF character that allows callers in a queue to be transferred to a voicemail or to be transferred in another predefined way.
The default value is the pound (#) key.
You can transfer callers to the voicemail in the following ways:
-
By selecting the Transfer to Voicemail if Queue Is Full option in
-
By choosing VOICEMAIL for the Forwarding Number after DTMF Character field in
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Number of Agents Affect Queue Size
Enter the value to define how the number of available agents affects the maximum size of the queue.
que len = max que len + (QueueLenSlope x available opers)
max que len means the queue size defined in the queue configuration.
The value for this setting can be one of the following:
-
x = 0 -> No effect (the configured static queue size).
-
x is greater than 0 -> More agents, longer queue.
-
x = 1 -> One additional agent means one more queue place.
-
x is smaller than 0 -> More agents, shorter queue.
The default value is 0.0.
E-mail
Max. Number of Unhandled E-Mails
Enter the number to define how many unallocated e-mails there can be before CEM stops reading new e-mails from the mail server. The default value is 2000.
Voice
Allow Routing to Closed Overflow Queue
Select this option if you want that calls can be routed to an overflow queue even when the overflow queue is closed according to a schedule. Usually calls are never routed to closed queues but in some cases, you may want the callers to hear the ServiceClosed prompt file.
Voice
Reference Timestamp for Calculating Queueing Time
Choose the timestamp to be used for calculating call priorities. The priority affects call allocation, see Allocation Priority Calculations. The default value is Call Enters Contact Center 1st Time.
-
Call Enters Contact Center 1st Time: Queuing time starts when the call enters the contact center application for the first time. The Welcome and Prewelcome messages are included. If the call is transferred from a queue or application to another (for example from the contact center to an IVR), the time is not reset.
-
CEM Receives Call Information: Queuing time starts when CEM Server gets the CALL_COMING message. If the call is transferred from a queue or application to another (for example from the contact center to an IVR), the time is not reset.
-
Call’s Last Entry to Contact Center: Queuing time starts when the call enters the contact center for the latest time. The Welcome and Prewelcome messages are included. If the call is transferred from a queue or application to another (for example from the contact center to an IVR), the time is reset.
-
Call Enters Queue: Queuing time starts when the call enters the current queue or application for the latest time. The Welcome and Prewelcome messages are not included.
Voice
Show Original Source Number to External Agents and MTD Devices
Select this option if you want that external agents see the original external source number when a call is transferred from a queue.
This is an operator-specific function and is supported by certain hardware only.
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Block Rejected Contact from Agent
For voice and chat channels:
Choose from the following options whether an auto-allocated queue contact can be re-allocated to the agent, who has rejected the contact or who did not pick it before either Timeout for Contacts to be Picked or Rejected or Answer Timeout for Queue Contacts expired. Note that if a contact is forwarded into another queue, the contact can be allocated to the same agent again.
-
Yes: Blocks all re-allocations from the queue.
-
Never: The contact can be offered to the same agent several times.
-
No Blocking if Contact Redirected after Max Waiting Time: Depends if the queue forwarding options Forward if All Agents Have Absence Profile or Are Logged Off from Queue or Forward if Allocating Is Not Possible Immediately is in use:
-
If none of the above mentioned queue forwarding options is in use, behaves as Never.
-
If one of the above mentioned queue forwarding options is in use, behaves as Yes.
-
For e-mail channel:
To block all re-allocations the queue, select the checkbox.
By default, this option is not selected.
Chat
Timeout for Idle Chats
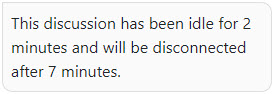
Enter a value to define how soon idle chats are removed. A chat is considered idle when there is no active text or video session in progress. The minimum value is 3 minutes and the maximum is 1 day. The default value is 10 minutes.Chat Warning Time for Idle Session Define a time after which a prompt message is sent to inform the customer that the chat has been idle and will be disconnected when the time you defined for Timeout for Idle Chats is reached. Use the prompt type Idle Session Warning Message and the variables Idle Session Duration and Warning Time for Disconnection. For more information, see Creating Prompts.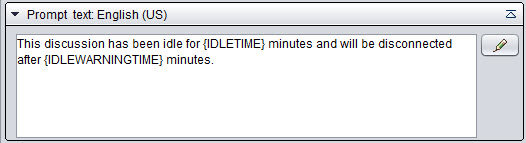
Chat
Busy During Wrap-Up
Select this option if you want the a chat session in the wrap-up mode is considered as an active chat session and counted to the Maximum Number of Chat Sessions value defined in .
example:The setting Busy During Wrap-Up is enabled either at the channel or queue level. The Maximum Number of Chat Sessions value is 3, and an agent has two active chat sessions and one in the wrap-up mode. The agent is not offered a new chat request until the chat session in the wrap-up mode is handled.
Voice
Max. Waiting Time for Preferred Agent
Enter a value to define how long the software waits for the preferred agent to be available before the call can be allocated to another agent. Calls are primarily offered to totally free agents. This function works only in a call transfer during one call event.
The default value is 20 seconds.
For example, the preferred agent can be the last agent who answered the call. This is useful when a blind transfer fails and the call comes back to the queue. Then the software tries to reallocate the call to the same agent. In the hunt group mode, another agent is still able to take the call before this time has elapsed.
The preferred agent function is automatically enabled.
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Skill Expiry Time
Enter a value to define how long time a skill requirement is valid. After this expiry time the contact can be allocated also to other agents if there has not been any agents available with the required skill level. The other option is to use skill reduction, see Defining Skill Reduction Values.
The default expiry times are:
-
For phone calls: 10 minutes
-
For e-mails: 1 week
-
For chat contacts: 10 minutes
E-mail
Default Expiry Time for Required Agent
Enter a value to define how long the Required Agent requirement is valid. After this expiry time the contact can be allocated also to other agents if the required agent has not been available. The default value is 1 week.
Table 2. Transfer Settings Channel Type
Field
Function
This group is for voice channel only.
Voice
Enable Transfer-On-Hold When Busy
Choose whether an agent can receive another call immediately after transferring an active call to a mobile phone or to an external number. In a normal situation, no calls are offered to the agent when this type of a target number is busy. This option has effect only if the transfer-on-hold method is in use.
Voice
Timeout for Transfer-On-Hold
Enter the timeout for calls that are not answered. This is only useful if the transfer-on-hold method is in use. If the call is not answered within the defined time, the call is considered as failed and CEM informs the Communication Desktop (CDT) or Communication Panel (CP) application that there was no answer. If the user wants to try the transfer again, the attempt must be repeated manually. The default value is 3600 seconds.
Voice
Enable Join Transfer
For advanced use only. Choose whether an alternative call transfer method is in use. In this case, CEM keeps the original call to the first destination waiting and initiates a new call to the second destination. These two calls are not connected until the new call to the second destination is successfully connected.
Voice
Timeout for Join Transfer
For advanced use only. Enter the timeout for calls to be connected to an external number. See the Enable Join Transfer option. The default value is 30 seconds.
Voice
Enable Barring of Internal Transfers
By default, internal transfers are not barred in a location that is used as a barring group. To enable barring internal transfers as well, select this option.
Table 3. Reporting and Monitoring Settings Channel Type
Field
Function
Voice, e-mail, and chat
False-Attempt Limit
Enter the threshold time limit that determines if a contact was a false attempt (not abandoned). Affects Service Level calculation, see below.
The default values are as follows:
-
For phone queues: 5 seconds
-
For e-mail queues: 0 (not in use)
-
For chat queues: 30 seconds
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Answered-on-Time Limit
Enter the time limit that determines if a contact was answered on time. Affects Service Level calculation, see below.
The default values are as follows:
-
For phone queues: 20 seconds
-
For e-mail queues: 60 minutes (1 hour)
-
For chat queues: 60 seconds (1 minute)
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Max. Handling Time
For advanced use only. Enter the maximum value used in the reporting. If a contact’s handling time exceeds this time, the contact is not included in reporting but it is listed as an exception in Data Transformation Engine (DTE) Reporting.
The default values are as follows:
-
For phone queues: 10 hours
-
For e-mail queues: 30 days
-
For chat queues: 4 hours
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Max. Waiting Time
For advanced use only. Enter the maximum value used in reporting. If a contact’s waiting time exceeds this time, the contact is not included in reporting but it is listed as an exception in Data Transformation Engine (DTE) Reporting.
The default values are as follows:
-
For phone queues: 1 hour
-
For e-mail queues: 30 days
-
For chat queues: 2 hours
Service level of a contact center or a specific queue is calculated as percentage of contacts answered-on-time of arrived contacts, false attempts are not included, SL = 100% x calls answered on time / (arrived calls-false attempts).
Table 4. E-Mail Settings Field
Function
Time Limit for Accepting E-Mails
Enter a time value to define the maximum time an agent has to react to allocated e-mails. If the agent does not react within the time limit, the e-mail is returned to the queue. If the value is changed, it does not affect the e-mails that have been already allocated.
The time limit value is based on a schedule time. For example, if the limit value is 1 week and the queue is open from 09:00 to 17:00, the limit is not reached after 1 week because the time the queue is closed is not calculated into the limit value.
Values are as follows:
-
0 = not in use
-
1 = a week
-
Other numeric values are interpreted as seconds.
The default value is 1.
In advanced use, the parameter can also refer to an external SOAP, COM or Python call. For more information, contact Sinch.
Customer Information
Enter a value to define how the external customer info should be determined.
In advanced use, the parameter can also refer to an external SOAP, COM or Python call. For more information, contact Sinch
Use Required Agent Instead of Preferred Agent
To use the required agent function instead of the preferred agent function, select this option. To define the waiting time for the required agent, use the setting Default Expiry Time for Required Agent in one of the following places:For more information, see Required Agent.- , in the E-Mail Settings block
- in the E-Mail Settings block.
Default Expiry Time for Required Agent
Enter a value to define how long the Required Agent requirement is valid. After this expiry time the contact can be allocated also to other agents if the required agent has not been available. The default value is 1 week.
Preferred Agent
To prefer the agent that has been in the related e-mail conversation before, use the value 1. To allocate the e-mail for the first appropriate agent, use the value 0. Other values are reserved for customized use.
When the preferred agent function is used, the e-mail goes automatically to the preferred agent’s pending list in CDT.
In advanced use, the parameter can also refer to an external SOAP, COM or Python call. For more information, contact Sinch.
Block E-Mail from Addresses
Enter a comma-separated list of addresses and names you want CEM to filter out. This means that e-mails from these persons are blocked. By default, this kind of spam filter is not used.
In advanced use, the parameter can also refer to an external SOAP, COM or Python call. For more information, contact Sinch.
Language Definition Method
Enter a custom method name for setting the e-mail language. By default, the queue or extension language is used.
In advanced use, the parameter can also refer to an external SOAP, COM or Python call. For more information, contact Sinch.
Old E-Mails Deleted After (d)
Enter the number of days after which CEM removes e-mails from the Received folder on the IMAP mail server. The default value is -1, which means that the setting is not in use.
Priority Definition Method
We recommend defining e-mail priorities with keywords instead of using this option, see Creating E-Mail Keyword Rules.
In advanced use, it is possible to set the e-mail priority with a custom method. By default, the queue or extension priority is used. The parameter can also refer to an external SOAP, COM or Python call. For more information, contact Sinch.
Table 5. Advanced Settings Channel Type
Field
Function
Voice
Delayed Acceptance Time
Enter the time that Call Dispatcher (CD) delays the sending of CALL_ACCEPT.
Voice
Display Original External Source Number
Select this option if you want that CEM attempts to display the original external source number (A number) when it transfers a call from a queue to an external number. Normally it displays the queue number as the source number. The R number is an operator-specific function and requires a special hardware configuration. For more information, contact Sinch.
Voice
Indicate if Original External Source Number Is Unknown
Select this option if you want that CEM indicates whether the original external source number (A number) is unknown when CEM transfers a call from a queue to an external number. Normally it displays the queue number as the source number. An unknown number means that the A number is hidden (CLIR, Calling Line Identification Restriction, is used).
E-mail
Find E-Mail Address of Sender
For advanced use only. Select this option if you want that the software tries to find the address of the real sender of the e-mail (for example from the e-mail body text).
This setting has no default CEM action since it can also refer to an external SOAP, COM or Python call only. Even when the option is selected, CEM uses the sender of the e-mail. By default, the option is not selected.
E-mail
Find Name of E-Mail Sender
For advanced use only. Select this option if you want that the software tries to find the name of the real sender of the e-mail (for example from the e-mail body text).
This setting has no default CEM action since it can also refer to an external SOAP, COM or Python call only. Even when the option is selected, CEM uses the sender of the e-mail. By default, the option is not selected.
Table 6. Extra Data Settings Channel Type
Field
Function
E-mail
Extra Data Included When E-Mail Allocated
Enter a comma-separated list of field names (for example Language, Skills, or any custom key-value pair to define host application specific data added in Task Management Interface) that are sent to the user interface when an e-mail is allocated to an agent. This setting is used with Embedded Communications Framework (ECF) and is also available in the queue view at when you select an email queue and open the Contact Management block.
Voice
Extra Data Included When Allocating Calls
Enter a comma-separated list of field names (for example CallerID, IVRInfo, Skills, Language, Class, CallGUID, ExternalData) that are sent to the user interface when a call is allocated to an agent.
The data may contain information collected by an IVR application and items like call GUID, skills, language, and so on. This data can be used by ClientCOM or JavaScript customizations.
Voice
Extra Data Included in Outbound Calls
Enter a comma-separated list of field names that are sent with outbound calls, transferred calls, and consultation calls.
The following fields are always automatically sent with consultation calls: FirstANumber, FirstBNumber, FirstAName, FirstBName, CALL_ID, CallGUID, CallReason. The default value is "" (only the default fields are sent).
Note: To pass this information to external number, define the settings , see Managing Trunks.Voice
Extra Data Included When Connecting Calls
Enter a comma-separated list of field names (for example CallerID, IVRInfo, Skills, Language, Class, CallGUID, ExternalData) that are sent to the user interface when a call is connected.
The data may contain information collected by an IVR application and items like call GUID, skills, language, and so on. This data can be used by ClientCOM or JavaScript customizations.
Voice
Extra Data Included When Supervising Calls
Enter a comma-separated list of field names (for example CallerID, IVRInfo, Skills, Language, Class, CallGUID, ExternalData) that are sent to the user interface when a call is being supervised in Communication Desktop (CDT). This setting does not apply to Communication Panel, where the supervisor sees the same extra data as the supervised agent.
The data may contain information collected by an IVR application and items like call GUID, skills, language, and so on. This data can be used by ClientCOM or JavaScript customizations.
Voice
Extra Data Included When Completing Consultation Calls
Enter a comma-separated list of field names (for example CallerID, IVRInfo, Skills, Language, Class, CallGUID, ExternalData) that are sent to the user interface when a consultation call is completed.
The data may contain information collected by an IVR application and items like call GUID, skills, language, and so on. This data can be used by ClientCOM or JavaScript customizations.
Voice and chat Extra Data Included in Statistics Enter a comma-separated list of field names you want to store in the database and to be visible in the History view of Communication Panel and in reports. Note the following about this setting:
- It is not recommend to store data that would include sensitive data.
- If this setting is empty, nothing is saved.
- For chats:
- Using the asterisk (*) saves all extra data.
- Extra data must be included before the chat conversation is answered by an agent.
- Name and email are removed from the attached data.
- Users need Statistic Details rights to view extra data in Communication Panel.
- For chat conversations extra data is not stored if the chat is not allocated to an agent; it is considered as an abandoned conversation.
Table 7. Weight Value Settings Channel Type
Field
Function
Note:-
To increase the importance of a parameter, set the weight value above 1, and to decrease the importance, set the value from 0 to 1.
-
When you adjust weight value settings take into consideration other parameters that affect allocation. For example, if you use skills in your system and you use the value 20 for Importance of Contact Waiting Time, the importance of the contact’s waiting time increases so much that skills are practically ignored. See Allocation Priority Calculations.
-
For more information, see Priority.
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Importance of Contact Waiting Time
Enter a value to define how important the contact’s waiting time is when selecting a next contact for a free agent. The default value is 1.
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Importance of Agent's Waiting Time
Enter a value to define how important the agent’s waiting time is when selecting an agent for a contact. The default value is 1.
This setting has an effect only if there are two or more agents available.
You can also use Target Time for Agents with Low Skill Levels in Miscellaneous Settings for adjusting the similar setting.
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Importance of Agent Priority
Enter a value to define how important the agent priority is when selecting an agent for a contact or a contact for an agent. A greater value than 1 increases importance, and a value smaller than 1 decreases the importance. The default value is 1.
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Importance of Skill Matching
Enter a value to define how important the skill matching is when selecting an agent for a contact or a contact for an agent. The default value is 1.
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Importance of Contact When on Same CEM as Agent
Note:Typically, this does not concern Sinch Contact Pro cloud.
Choose a value to define the importance of a contact when the contact is on the same CEM as an agent. The default value 1.00 which means that all contacts on different CEMs have the same priority. A greater value than 1 means that the contact on the same CEM is more important.
This setting can also be defined at the queue level.
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Importance of Agent When on Same CEM as Contact
Note:Typically, this does not concern Sinch Contact Pro cloud.
Choose a value to define the importance of an agent when the agent is on the same CEM as a contact. The default value 1.00 which means that all agents on different CEMs have the same priority. A greater value than 1 means that the agent on the same CEM is more important.
This setting can also be defined at the queue level.
For more information about how priority values can be used in the system, see Priority.
Table 8. Recording Channel Type
Field
Function
Voice
Recording Behavior with Consents
Select how customer consents are used in recording:
-
Ignore Consents: Customer consents (the ones asked for a current call with an IVR, nor the ones saved in database earlier, or imported from an external system) do not affect recording. The default value.
-
Ask For and Follow Customer Consent: If customer consent is not found in database, it is asked with an IVR. Calls are recorded only if there is a customer consent to record the call. If you select this option on the channel level, consent question is asked in all inbound calls, both direct and queue calls, assuming that proper prompts are added, and the IVR number defined. For more information, see Consent IVRs.
Voice
Consent IVR Number
Select or enter either the built-in consent IVR number defined in , or the custom IVR number defined in IVR Management. This consent IVR is then used for all phone queues in the system, unless a queue-specific value is defined.
This number can be defined for the entire system on the channel level though the consent IVR is used only in queue calls, or some specific queues. In that case choose Ignore Consents on the channel level, and the option Ask For and Follow Customer Consent in a queue's contact management.
Table 9. Miscellaneous Settings Channel Type
Field
Function
E-mail
Send Autom. Reply Only on First Allocation
Select this option if you want that the first allocation triggers an automatic reply if an e-mail is allocated several times.
E-mail
Max. Number of Unhandled E-Mails per Agent
Enter a value to define how many unhandled pending e-mails an agent can have in the channels controlled by CEM. The default value is 50.
All active e-mails must have the Pending status in the Communication Desktop (CDT) or Communication Panel (CP) application before CEM allocates more e-mails to an agent.
Voice
Max. Number of Allowed External Call Loops
Enter the maximum number of allowed external call loops.
For example, you call agent A that has a direct transfer to number B. Then there is a call transfer to number C, and again there is a transfer back to the A number that has a direct transfer to number B, and so on. If the number of loops (calls from the same A number to the same B number, and forwarded to the same C number) is greater that the value of this setting during the time defined with the Timeout for Allowed External Call Loops setting, the extra calls are disconnected. The C number must be a direct number. The default value is 4.
Voice
Timeout for Allowed External Call Loops
The default value is 60000 milliseconds.
Voice
No. of Queue Calls Sent to and Displayed on Virtual Phone
Note: This setting is related to hunt group queues which are not supported in Sinch Contact Pro.Enter the number of calls in a queue that are sent from CEM to the virtual phone and displayed in the order of priority when an agent logs into the queue.
This limitation saves resources and applies to all hunt group queues. The default value is 5.
example:An agent serves in the following hunt group queues: Q1 (has 3 calls), Q2 (has 5 calls), and Q1 (has 1 call). If the default value 5 is used, CEM sends 3 calls from Q1 and 2 calls from Q2 to the user interface. Rest of the calls are not displayed.
Voice
Ringing Time for Agent's Direct Queue when Agent Busy
Enter the ringing time used in the agent’s direct queue instead of the normal ringing time.
Voice
Timeout for Virtual Channel
Enter the time for a timeout. If the connection to a terminal client or to the module that controls external terminals (ETC) is disconnected unexpectedly, the session of the disconnected client is put to a paused status. If the connection is not restored during the timeout, the system forces an agent to log out. The default value is 120000 milliseconds.
Voice
Unavailability Time During Transfer-On-Hold
Enter a value to define how long an agent is reserved for the transfer before the next call is possible. The default value is 5 seconds.
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Target Time for Agents with Low Skill Levels
Enter a value to define how often an agent with the lowest level of skills should have contacts. This ensures that no agent is left without contacts (but if a skill requirement for the contact is 5, the contact is never allocated to an agent without the required skill).
Increase the value to make this waiting time less important. The default value is 24 hours.
You can also use Importance of Agent Priority in Weight Value Settings for adjusting the similar setting.
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Use Absolute Waiting Times in Skill Reduction
Select this option if you want that the defined skill reduction values are always used. Otherwise, if there are no agents with the required skill level serving in the queue, the requirement is lowered to match the highest skill level of a serving agent.
For more information about skill reduction, see Defining Skill Reduction Values.
Voice, e-mail, and chat
Extend Skill Reduction
Select this option if you want that the reduction applies also to skill requirements that have not been defined for the queue. This includes skill requirements set in the previous queue or by IVR, email keywords, and requirements set via interfaces (Online Integration Interface (OII) or Task Management Interface (TMI) ).
For more information about skill reduction, see Defining Skill Reduction Values.
E-mail
Timeout for Open Emails
Enter a value to define when open email channel conversations are set to the pending state. This means the conversations, both emails and tasks, that are open because the agent has signed out or the browser session is abruptly closed. The conversations are therefore automatically saved. If the agent (current conversation owner) signs back into Communication Panel before the set Timeout for Open Emails time has elapsed they can continue.
If the conversation owner remains signed out and the timer elapses, the conversation is put automatically to a pending state for picking by others also.
The default value for the timeout is 1 day.
Note the following:
-
Although the system looks for open email channel conversations of signed-out agents to be set to the pending state approximately every one minute, the interval can be some seconds longer due to, for example, network or database slowness.
-
When CEM starts, the signed-out timestamp of an agent is the time the first one of the agent's conversations is registered with the routing engine. This means that at the earliest the conversation status is set to pending is after the time defined in the timeout setting added with 1,5 minutes.
- Save your entries.
